Parking effects all land uses and landscapes in Chester County.
How it Works
Parking lots serving shopping centers, office complexes, and industrial uses often contain an excessive number of parking spaces. Seldom used areas within parking lots represent an inefficient use of land and underused parking facilities create an unnecessary increase in impervious cover, resulting in additional stormwater runoff. The increase in impervious cover and runoff has the potential to limit groundwater recharge and increase downstream flooding. An overabundance of parking facilities can also result in unnecessary financial responsibilities associated with maintaining parking lot surfaces, landscaping, and lighting.
In addition, roadways in Chester County are becoming more and more congested. The opportunities to relieve congestion through construction of new roads are very limited and costly. Travel demand management is a means to mitigate congestion by giving commuters opportunities to get to work by means other than driving alone in an automobile. One means by which this can be accomplished is through carpooling and the use of park and ride lots at key locations.
Benefits
Parking management plans can provide the following benefits:
Efficiency
Parking management plans can maintain optimum levels of parking.
Reduces Cost
Parking management plans can offset the cost of a parking program in village, downtown, or urban areas.
Increases Cooperation
Parking management plans can create cooperative efforts and open dialogue between the local government and the business community.
Alternative Parking Opportunities
These plans can provide opportunities for alternative parking programs such as park-and-ride lots.
Revitalization
These plans can represent important roles in downtown revitalization efforts.
Pedestrian Access
Parking management plans can provide opportunities for pedestrian safety and access strategies by locating on-street parking in areas where goods and services are located, which may slow vehicular traffic to speeds safer for pedestrian crossing.
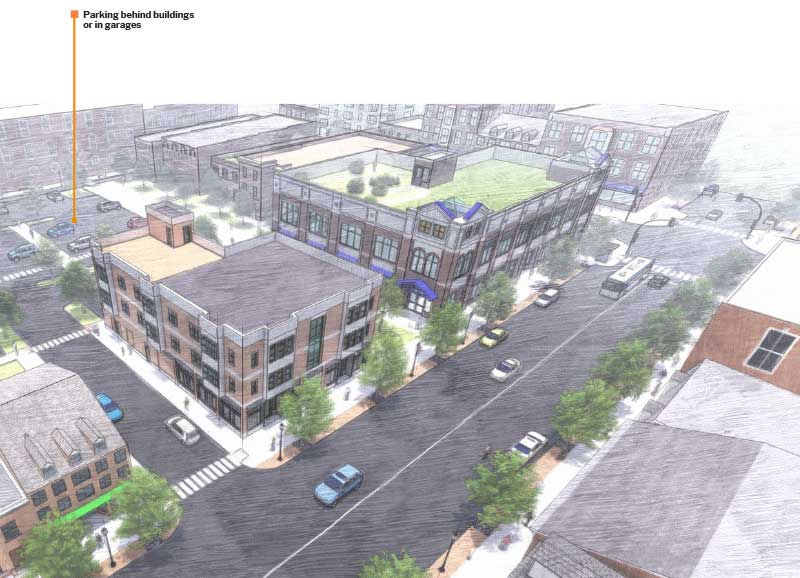

Proper parking management planning makes access easier for both vehicles and pedestrians.
Park and ride lots can provide the following benefits:
Energy Efficiency
Park and ride lots can lead to reductions in vehicle miles of travel, energy consumption and vehicle emissions.
Encourages Public Transit Opportunities
While many communities would like to establish some form of public transportation for their residents and commuters, few municipalities have the development density to financially support public transportation. A heavily used park and ride lot can create a critical mass which would then lead to the development or extension of a bus route.
Reduces Congestion
As major highways are reconstructed, congestion can be mitigated through the expansion of ridesharing, which is further enabled with the provision of Park and Ride lots.
Get Started
A parking management program can ensure that a municipal parking system operates as efficiently as possible, provides an adequate number of parking spaces, and is effectively managed. To achieve this, a parking management program is used to evaluate parking supply, determine current and future parking requirements, evaluate current policies, and implement plans to meet current and future parking needs.
A parking management program is usually associated with urban centers where on-street parking and parking fees are typical. However, parking management should be viewed from a wider perspective as it can relate to a variety of areas. Many municipalities, whether urban or suburban often discover that certain areas or uses have either a surplus or a deficit of available parking or find that there are concerns with the management or use of parking facilities. In urban centers, it is not uncommon to have parking deficit problems where older and more compact development patterns exist without considering today’s auto-dependent society. The apparent lack of parking or inaccessible parking in a downtown or commercial center is often viewed as a major reason for the decline of downtown commercial business. Equally important, a parking deficit in a commercial area can cause parking to overflow into nearby residential neighborhoods.

Parking management is particularly important in urban centers.
Process
A parking management program can be created to analyze an individual parking problem or to establish a long-term municipal program. The preparation of a study to address an individual problem includes establishing objectives of the program, evaluating the existing parking system, specifying actions to address the objectives, and identifying methods to implement the actions. A long-term municipal parking management program can require the collection and analysis of the same information as an individual study but will require day to day attention and periodic evaluation to determine whether current actions are meeting parking goals.
It is essential to clearly define the objectives of the program. Clearly defined objectives will make it easier to develop the most effective actions. Objectives will vary significantly from place to place and will depend on individual circumstances, local goals, personnel limitations, development opportunities, and available funding.
A variety of information will be useful to effectively evaluate the existing parking system including the current availability of parking, public perception of parking conditions, identification of public parking needs, and current parking policies.
Considerations
Increasing available parking for retail customers
Retail uses depend on parking to provide easy access for customers. Although it is sometimes more a perceived problem than an actual problem, insufficient parking is often considered a major issue by retail business owners in urban and commercial centers. Increasing parking availability in urban and commercial centers can be achieved through increasing parking turnover rates in prime parking areas or by educating local employees about the importance of parking in less vital areas.
Increasing parking turnover
Where available parking for retail customers is a concern, then the Plan should identify methods to increase the parking turnover rate in prime parking areas. A particularly useful way of increasing the rate of parking turnover is through a properly planned and enforced parking fee system. Parking fees should be established that provide disincentives for long-term parking in prime parking locations while providing options for lower fee, long term parking at convenient, but more distant locations.
Wayfinding signage for parking areas
Parking wayfinding helps drivers find a parking space more efficiently without cruising the area for available parking. This can save visitors from unnecessary frustration, lower congestion, and lessen opportunities for conflicts with pedestrians and bicyclists. The township of Montclair, New Jersey's draft parking management plan includes many examples of wayfinding signage for parking.
Enforcement of parking regulations
Proper enforcement of parking regulations is an essential part of an effective parking program. Enforcement will assist with generating revenue and will increase parking turnover in prime locations. Optimal revenue will be generated by ensuring that parking fees are generally being paid and fines are being issued to enforce parking regulations.
Improving the revenue generating capabilities of parking facilities
The costs associated with developing many parking management programs can be offset by a parking fee schedule. Periodic evaluation of fee and fine schedules should be included to ensure that fee and fine schedules are not too excessive but are adequate to assist in meeting their intended purposes. Excessive fees can be detrimental to the economic competitiveness of an urban or retail center.
Long term evaluation of parking availability
It is necessary to monitor parking conditions. As land uses in the urban centers change and as commuting habits of people change, parking requirements or issues may also change. A parking management plan should provide on-going evaluations to provide the flexibility to accommodate changes.
Evaluating current parking requirements
Municipal zoning and subdivision and land development ordinances include parking requirements for specific land uses and are typically based on national or regional studies of general land use classifications. Municipalities should consider updating parking requirements to more closely match local needs and specific types of land uses. Studying local uses or uses that are more closely related to a proposed use may identify where parking requirements can be adjusted. Historically, uses such as shopping centers, apartment complexes, senior housing, and offices have had large parking areas. With changes in where people work, how they shop, and increases in the use of micro transit services, the amount of parking required for these uses may need to be revisited.
Parking Maximums
One methodology that may be useful to better address parking requirements is the establishment of parking maximums. Parking maximums set an upper limit on parking supply, either at the site or across a larger area or district. Either type of maximum can be imposed in addition to or instead of minimum parking requirements. Establishing a maximum allowable amount of parking can prevent developers from building excessively large lots or link the parking supply in an area to roadway capacity or community priorities. Communities looking to increase tax revenue through redevelopment of parking lots, improve pedestrian safety and comfort downtown, or reduce stormwater runoff and heat islands should consider parking maximums as a way to achieve those goals.
Parking Supply
An inventory of existing parking and a data-informed estimate of future parking needs should be incorporated into the parking management planning process. Communities seeing growth in their downtowns may find the need for additional parking through the addition of a parking garage or municipal parking lot.
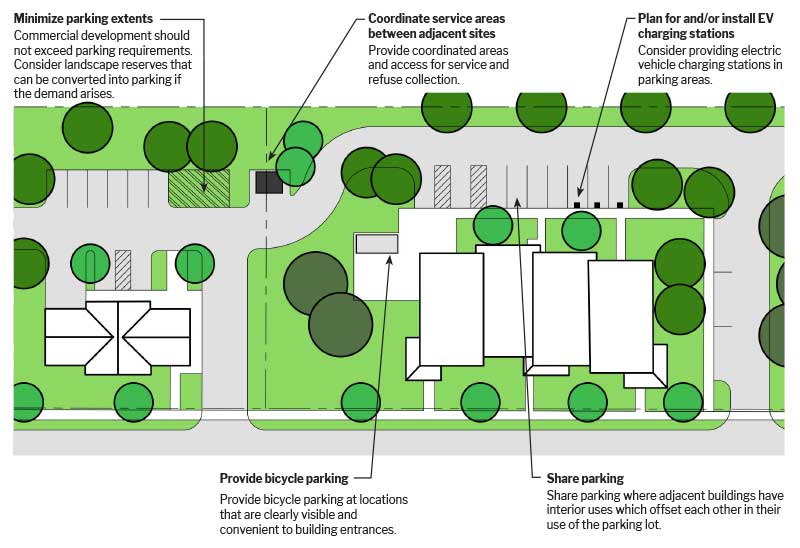
Shared and interconnected parking lots assists drivers while limiting driveway access points to exterior roads.
Possibilities for shared parking facilities
Municipalities should consider possibilities for shared parking facilities based on operating hours and peak parking times for adjacent or nearby uses. Through the use of shared parking facilities, a lower overall number of parking spaces may be justified. Municipalities should be assured that adequate parking facilities for all uses will continue in the long-term and be available regardless of individual land use changes. Phoenixville's Parking Management Plan addresses the benefits of shared parking facilities in the section titled, "Future Near-Term Parking".
Nearby transit opportunities
In determining the need for parking facilities, a municipality should consider the proximity of public transit opportunities such as bus stops, rail stations, and park-and-ride lots. Transit facilities in an urban center can lessen the demand for parking because employees, clients, or customers can avoid using automobiles. However, the transit facility itself will require parking to accommodate the transit users who drive to the facility.
Alternatives to permanent impervious parking facilities
Parking lots associated with shopping centers and malls are typically created to accommodate the number of cars expected on the busiest days of the year. As a result, for most days of the year there is an abundance of unused parking spaces. Municipalities should consider reducing the number of required paved or asphalt parking spaces and require a combination of paved and non-paved spaces. For example, grass pavers can be used to create a stable pervious parking area that does not require blacktop. Porous paving is another alternative to impervious surface parking. Although porous paving does not reduce the amount of paved surface, it does assist with stormwater control and groundwater recharge. These grass-paved areas could serve as reserve parking and be used to accommodate visitors for events.
"Fee-in-lieu of parking" programs
A "fee-in-lieu of parking" program could be considered in areas where parking is limited due to space constraints and additional funds are needed to build and operate municipally owned parking facilities. In such instances, a municipality can reduce or waive parking requirements in exchange for funds that are dedicated to establishing or operating public parking facilities.
Incentive programs to alleviate parking needs (ride share, flexible hours, telecommuting)
Municipalities should be willing to consider alternatives to reduced parking requirements where applicants can justify that a reduction in parking results from changes in business operations and technology such as flextime and telecommuting. A municipality must receive a long-term commitment from the developer to be assured that the reduced parking will accommodate future demand. If a commitment cannot be made, then the developer could be permitted to build a portion of the required parking and establish an escrow fund for the remaining portion.
Marketing parking programs
Increasing public knowledge and awareness about the parking locations, policies, and regulations through the use of marketing programs will help to assure that parking facilities are used to their fullest capability. Local business owners and employees should be educated about the benefit of parking in non-critical parking areas in order to reserve critical parking areas for local customers. Adequate use of signs and flyers can be used as marketing tools to assist in identifying the location of parking areas, to help educate the public about parking regulations, public parking facilities, and public transit opportunities.
One of the most common forms of travel demand management is ride-sharing such as carpooling. A park and ride lot is a parking area that is used by commuters to share a ride to work or to use public transportation.
Park and ride lots come in different forms including:
- A parking lot that was constructed for other uses such as a shopping mall but is being informally used for ride sharing;
- A parking lot at a shopping center or church which has been formally leased for use by commuters; or,
- A lot which has been constructed by a public agency exclusively for use by commuters.
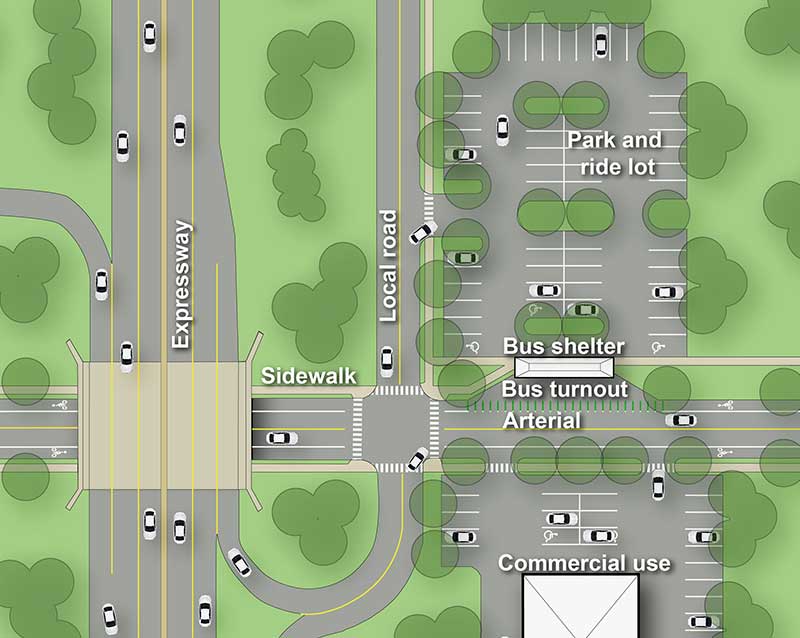
Typical park and ride lot.
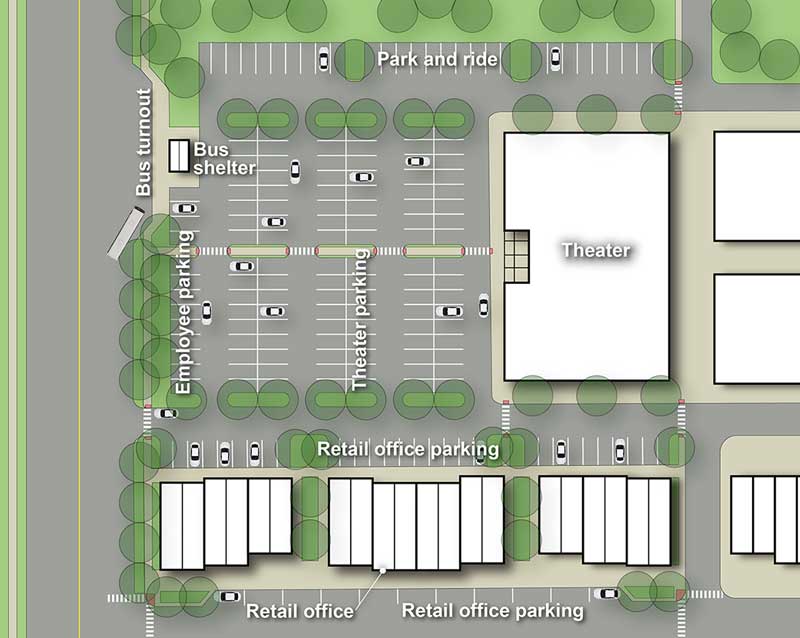
Example of a shared parking facility
Process
Historically in Chester County, the process of implementing a park and ride lot starts when municipal officials notice a pattern of commuter parking along highway interchanges or in commercial areas. Municipal officials then notify the County Planning Commission or the local transportation management association (TMA) of the potential for a lot and an investigation will determine the level of demand and feasibility. The County and TMA will then work with PennDOT to determine the best funding approach.
Historically in Chester County, the process of implementing a park and ride lot starts when municipal officials notice a pattern of commuter parking along highway interchanges or in commercial areas. Municipal officials then notify the County Planning Commission or the local transportation management association (TMA) of the potential for a lot and an investigation will determine the level of demand and feasibility. The County and TMA will then work with PennDOT to determine the best funding approach.
Considerations
- Park and ride lots must be designed with safe access into and out of the lot.
- Where possible, lots should be located near major highways interchanges and/or adjacent to existing or anticipated bus routes.
- Appropriate landscaping should be provided to mitigate the aesthetics associated with parking areas. The landscaping design should avoid unsightly expanses of pavement and should consider security as well as sight distance requirements.
- Street lighting should be included in the design of the project where security issues may be present.
- Municipalities should consider encouraging the dedication of spaces for park and ride in commercial uses during the land development process. For example, a cinema complex may be an excellent opportunity for day use as a park and ride lot.
- A promotional program is needed periodically to inform the public of the availability of the lot.
- If a lease agreement can be made with an existing facility such as a shopping center, the marketability of park and ride can be tested in that area before any major capital expense is made. If the lot has significant use, the lease can be extended, or a new lot could be constructed for public use.
Examples
City of Coatesville Zoning Ordinance
Article XIII, Off-Street Parking (Off-Street Parking Alternatives & Modification of Required Parking Spaces).
West Chester Borough Zoning Ordinance
Article XIII Parking and loading Regulations (Conditional reduction of off-street parking areas).
Borough of Phoenixville Parking Study
Parking Management Plan
Township of Montclair, NJ
Parking Management Plan



